LiDAR (Light Detection And Ranging): A form of representation of 3D surfaces, Point cloud data, are usually produced by aerial or terrestrial laser scanning, also known as Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR).
The data is produced as sets of very dense (x, y, z) points or in a more common, binary format called LAS that may include values of multiple returns and point intensities. Many leading GIS processing software’s now accommodate and supports basic and advanced LiDAR data processing and analysis. LiDAR is emerging as one of the cost-effective and accurate data capture system to manage large assets such as Railway stations and other public/private infrastructures.
SBL GIS Services division has been in the forefront of processing LiDAR services for some time now. Our LiDAR data processing services has been entrusted with prestigious and complex Infrastructure modelling projects across many geographies. One such example is demonstrated in the picture given below.
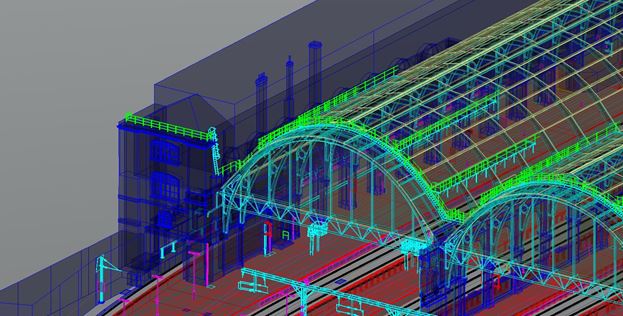
The Science behind LiDAR Working
LiDAR working is quite simple and it works on the principle of Light – speed and time taken to reflect the same from a surface. The distance is calculated from the difference between the time when a beam of light hits a surface and measure the time it takes to return to its source. Light travels very fast – about 300,000 kilometers per second, or 0.3 meters per nanosecond so we feel the instantaneous result when a light is turned on. The paraphernalia required to measure this needs to function extremely fast. Only with the advancements in modern computing technology has this has become possible.
Distance = (Speed of Light x Time of Flight) / 2
USES OF LiDAR MAPPING.
One of the main focus of LiDAR services in the Urban Infrastructure Mapping.
Urban Infrastructure Planning
Urban Planning or City development is the science of land use planning which considers several aspects of the as-built data and social environments of the area of interest. LiDAR Mapping is a moderately new technology for obtaining Digital Surface Models (DSMs) and Digital Building Models. This data, when combined with orthorectified images, can create highly detailed Surface Models and eventually 3D City Models.
Wayside assets include tarmacs, streetlights, signs, advertisement boards, traffic signals and street furniture. A thorough understanding of all the assets, what they are and where each asset is located, is crucial to the development of an asset portfolio.
An accurate record of all assets along the transportation network is vital to asset management, to plan a maintenance schedule and budget costs. A bigger challenge than developing the asset database is keeping it up to date and this is where the cost-effective, accurate LiDAR Mapping will come into play.
About the Author:
Anil Narendran Pillai – (Vice President – Geomatics @ SBL) Mr. Pillai heads the GSS (Geospatial Services) domain at SBL(www.sblcorp.com). He has worked in the digital mapping, remote sensing, and GIS industries for over 23 years. He has 23+ years experience managing and coordinating GIS projects and 12 years senior management experience. He has extensive experience in all aspects of aerial and satellite imaging technology and applications. He has utilized remotely sensed satellite and airborne imagery for a variety of environmental applications including site location analysis, forestry, telecommunications and utility corridor mapping. He has a strong background in management of GIS and Photogrammetry imaging projects to support Government and private industry needs.His Passion lies in Need Analysis and Documentation, Topographical Mapping (ArcGIS), Spatial Data Management, Integrity and Security, GIS Data transformations and projections from multiple sources, Image Processing Software user testing and documentation, Project Coordination and Tech. Support, Inter-agency communication and support, 3D Data Generation and Management,Project Management, Digital Photogrammetry, Satellite Image Processing, Pre-Sales Presentations.
Article provided with permission by www.sblcorp.com
See more about SBL LiDAR services http://www.sblcorp.com/Geospatial-Services/lidar-services.php
Original article and pictures take gisuser.com site
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий